The transistor is the most important invention in modern electronics. From amplifying signals in radios to powering microprocessors in computers, transistors form the foundation of every electronic device. In this complete guide, you’ll learn transistor basics, which include the following concepts :
- What a Transistor is and How it Works?
- Different types of transistors (NPN, PNP, etc.)
- Key parameters and specifications
- How to use transistors in amplifier, switching, and oscillator circuits
- A list of popular transistor models with datasheets
Whether you’re an engineering student, electronics hobbyist, or circuit designer, this guide connects all major transistor topics covered in WatElectronics.
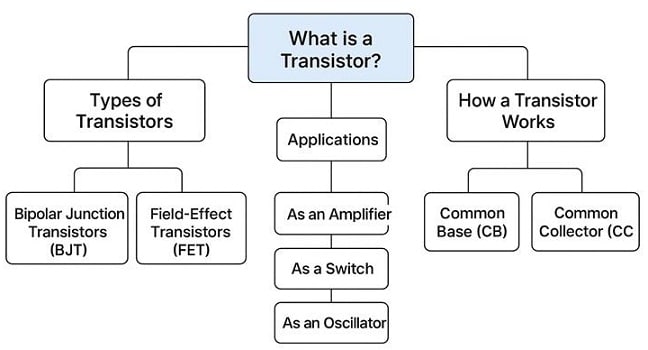
What is a Transistor?
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals. It has three terminals — Emitter, Base, and Collector — that control the flow of current. Transistors are made using silicon or germanium, where small changes in input voltage can cause large changes in output current, enabling amplification and control.
Transistor Basics Concept
Read more:
Types of Transistors
Transistors are mainly classified into two types:
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)
These transistors have both electrons and holes as charge carriers and come in two types:
- NPN Transistor – Used widely for amplification and switching.
- PNP Transistor – Used in complementary configurations with NPN.
Detailed Comparisons:
Field-Effect Transistors (FET)
Although BJTs dominate in analog applications, FETs (like MOSFETs) are used in digital circuits for fast switching and low power consumption.
Related read: MOSFET – Working and Types
How a Transistor Works
A transistor acts like a current-controlled switch or amplifier. When a small current flows through the base, it allows a significantly larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter.
For Example:
- In NPN transistors, current flows when the base is given a small positive voltage.
- In PNP transistors, current flows when the base is slightly more negative than the emitter.
In-depth Explanation:
- Transistor as a Switch – Circuit and Working
- Transistor as an Amplifier
Transistor Configurations
BJTs can be connected in three configurations, depending on the terminal shared between the input and output.
| Configuration | Common Terminal | Application | Gain Type |
| Common Base (CB) | Base | High-frequency amplifiers | Voltage gain |
| Common Emitter (CE) | Emitter | Audio amplifiers, switches | Voltage & current gain |
| Common Collector (CC) | Collector | Buffer circuits | Current gain |
Explore:
- Common Emitter Transistor Configuration
- Common Collector Configuration
Transistor Basics: Biasing Techniques
For reliable operation, the transistor must be properly biased to maintain its active region.
Common methods include:
- Fixed bias
- Voltage divider bias
- Emitter resistor bias
Learn more: Transistor Biasing Techniques
Transistor Basics – Applications
Transistors are found in thousands of applications — here are the most common:
1. As an Amplifier
Used in radios, audio systems, and communication circuits.
Transistor Amplifier – Working, Circuit, and Applications
2. As a Switch
- Used in relay drivers, LED control circuits, and logic level conversion.
- Transistor as a Switch – Examples & Calculations
3. As an Oscillator
- Used for generating signals in transmitters and timers.
- Transistor Oscillator Circuits
Popular Transistor Basics – Models and Datasheets
Below are some popular transistors with links to detailed pages:
| Transistor | Type | Description | Link |
| BC107 | NPN | Used in low-noise audio circuits | BC107 Transistor – Features and Applications |
| BC109 | NPN | High-frequency low-noise transistor | BC109 Transistor |
| BF194 / BF494 | NPN | Used in RF circuits | BF494 Transistor |
| TIP35 | NPN | High-power transistor | TIP35 Transistor |
| 2SC3358 | NPN | High-frequency amplifier transistor | 2SC3358 Transistor |
Advanced Topics
For readers wanting to go beyond basics:
- Difference Between BJT and FET
- Darlington Pair Transistor – Working and Advantages
- Transistor Parameters Explained
Related Concepts to Explore
- Semiconductor Basics – PN Junction Diode Working
- Types of Diodes and Their Applications
- Difference Between Diode and Transistor
Transistor interfacing:
The transistor can be interfaced with a microcontroller as well. Check on interfacing with the microcontroller
Selection of the base resistance of a transistor:
The base resistance of a transistor plays a vital role in its application. Read more on it in Selecting the base resistance of a transistor
Conclusion
Transistors are the heart of every modern electronic system. By understanding Transistor Basics – their working principles, types, and practical circuits, you can design everything from amplifiers to logic gates. To explore each type in detail, visit the linked transistor pages above — each article provides circuits, pin configurations, and applications tailored to your learning needs. Bookmark this guide and explore our complete Transistor Section on WatElectronics for detailed circuit examples and datasheets.