An amplifier can be considered as the basic electronic device. These amplifiers do exist in various types. Based on the operations performed in various modes and the types of configurations used the amplifiers are classified. The basic operation of these devices is to enhance and increase the strength of the applied input signal.
Amplifiers can be classified under various categories it may be an operational amplifier, small-signal strength, and large-signal or power amplifiers. These devices consist of a basic unit as transistors. There are three regions of operation in transistors. Among those three regions the transistor works in the active region, this makes it a good option for amplification of the signals.
What is an Amplifier?
The amplifier is the device that consists of its major component as a transistor. The devices that are used to perform the amplification of the applied input signals and which enhances the strength of the signal can be defined as amplifiers. For example in music players, in speakerphones, these amplifiers are used in various devices to enhance the strength of the signal. There are many practical examples of amplifiers. Even for long-distance communication or wireless communication, these devices are utilized.
Amplifier Circuit
A basic amplifier circuit consists of any type of transistor it may be BJT, FET or any other transistor. The designing of this amplification circuit is simple.
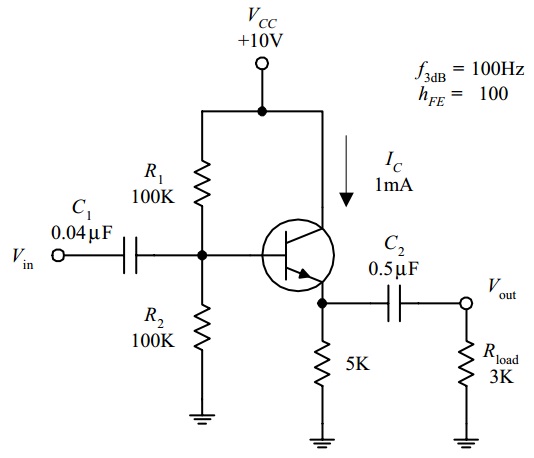
Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit
In the above circuit, common emitter configuration has been chosen in the design of the amplifier. The circuit consists of potential divider circuitry that consists of resistors at the input side for the applied input signal to pass through this circuit. The input signal is applied across the emitter and the base junction. The output is taken across the terminal called the collector. Here emitter is the common terminal present in both the input and the output sides.
Amplifier Construction
Let us consider a basic amplifier circuit with a bipolar junction transistor (BJT). BJT is of two different types N-P-N and P-N-P based on the type of semiconductor material chosen. In the above circuit, we have considered common emitter with N-P-N type. By connecting the resistors across the input and the emitter terminal along with that a resistor must also be connected across the output. Capacitors and the presence of the resistor in the circuit make the transistor to get biased properly. Once it will be done the amplification of the signal task will become efficient and simpler.
Amplifier Working Principle
The basic principle involved in the working of these amplifiers is that the applied input signal must be applied at the junction that must be forward biased. The output can be collected across the junction of reverse bias. The accurate measurement of the signal can be obtained through the above way.
The input side through which the signal is applied consists of a low value of resistance. The minimum amount of change in the input can produce an extreme change at the output.
Types of Amplifiers
Based on the size of the amplifier designed, and the processing of the signals amplifiers can be classified into various types. Each classification has its significance. Based on the type of the signal requirement its classification for the respective circuit has been chosen. Either the signal chosen can be of larger value or the smaller values.
| Signal Type | Configuration | Classification | Operation Frequency |
| 1.If the type of the signal is considered to be small | The type of configuration chosen is of Common Emitter. | Class A amplifier | Operates through the Direct current(DC) |
| 2. If the considered signals are of large type | The type of configuration can be of Common Base. | Class B Amplifier | Operates in the range of Audio Frequency. |
| The type of configuration can be of Common Collector. | Class AB Amplifier | Operates in the range of Radio Frequency | |
| Class C Amplifier | Operates at VHF, SHF, and UHF ranges. |
Generally, the classification is based on the variant of the signal. If it is of small-signal then these amplifiers can be utilized in the pre-amplification of the signals or as instrumentation amplifiers. While in the large signals amplifications the power must drive the load. Hence these are known as power amplifiers. These are connected to the output stages. In practical examples, these are seen in the output stages of loudspeakers.
The amplifiers can be chosen based on its operating frequency ranges. Each amplifier based on its operating frequency can be further classified into various classes. The amplifiers utilized in audio amplification are classified in the alphabetical order of the classes. The classification is characterized based on the applied input and the output relation and its characteristics.
Applications of Amplifiers
There are various practical amplifiers which have very prominent applications. Some of the applications of the amplifiers are:
-
Audio Amplifiers
The low values of signals that are generated from the microphones or any disks etc…are amplified with the help of voltage amplifiers. Other than this the amplifiers are known for performing the various functions such as Equalizers, tone corrector and so on.
-
Intermediate Frequency of Amplifiers
These amplifiers are known for operating in the mid-frequency ranges. These act as tuners in the circuits of radio sets, in the TV sets and so on. The purpose behind such kind of amplifiers is to provide the major values of the amplification of the signals in TV and the radar before the information carried out by the signals gets separated from the signals of radio.
-
Radio Frequency Amplifiers
These give very low noise and are preferred as the turners. These are preferred at the initial stages of the receivers. To drive the antennas of the respective transmitter these are used.
-
Ultrasonic Amplifiers
In this, the amplifier operates at the range of ultrasonic waves. The practical examples of this are seen in the ultrasound scanning for diagnostic services. These are also used in the remote control systems. But the limitation is that the system functioning should in the range of ultrasonic frequencies.
-
Direct Coupled Amplifiers
To amplify the frequency signals with the lowest values. The output obtained at one stage is coupled to another so that the frequency of the signal is increased. In the systems that are designed for measurement and the various control systems, these kinds of amplifiers are used.
The above are some of the applications of the amplifiers. The design of the amplifiers is simple and easy to construct. These have many advantages in the field of electronics. Various types of amplifiers can be used with various configurations. For each application there exist different types of amplifier. Can you tell me that operational amplifiers are preferred for what type of amplification?
Please refer to this link to know more about Audio amplifier circuit.