Sometimes, while performing electrical operations, it becomes important for us to isolate one part of the circuit to another to prevent excess loss of energy. For that reason, we use an isolation amplifier which acts as an isolating device. The main purpose of the isolation amplifier is to electrically separate the circuit which comes before the amplifier from the circuit which comes after the amplifier. So, basically we can say that an isolation amplifier can be used to give ohmic isolation between the output and the input terminals of the amplifier. In some cases, the isolation amplifier can also be used to amplify low-level signals.
What is an Isolation Amplifier?
Definition: An isolation amplifier is also known as a unit gain amplifier. It is basically an operational amplifier circuit which can be used to separate a section of a circuit from another. By doing so, it makes sure that power is not drawn or wasted in any part of the circuit. The isolation amplifier is not used to amplify the signal. The signal which is input to the amplifier and the signal which passes out of the amplifier is exactly the same which means that the input voltage remains the same as the output voltage. If the input voltage is 10 V AC, then the output is also 10V AC. The isolation amplifier diagram is shown below.
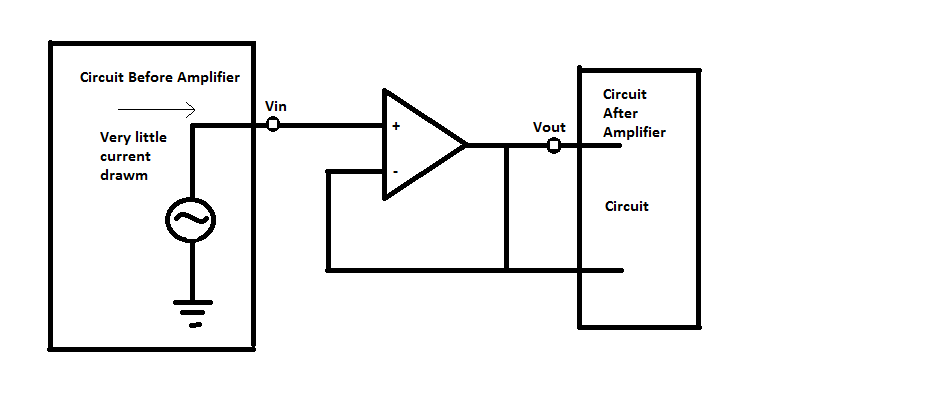
Isolation Amplifier
Isolation Amplifier Design Methods
There are three methods which are used to design an isolated amplifier. These three methods have been mentioned below:
Transformer Isolation
Transformer isolation uses either a pulse width modulated carrier signal or a frequency modulated carrier signal. Internally, the oscillator is 20KHz. Along with it, the device also has a rectifier, a transformer, and a filter that provides supplies for different isolated stages. The rectifier is used to provide input to the primary op-amp, the transformer can couple the supply, the oscillator is used to provide input to the secondary om-amp and the low pass filter removes the frequency components from the circuit.
Advantages
The advantages of transformer isolation include the following.
- It has high accuracy
- It has high linearity
- The common-mode rejection ratio is also quite high
Applications
The applications of transformer isolation include the following.
- Patient monitoring and diagnostic purposes in medical fields
- Ground loop elimination in industries
- Power isolation in nuclear power plants
Optical Isolation
In this type of amplifier, the biological signal is transformed into a light signal. This device has a patient circuit which is also the input circuit, and the output circuit is the phototransistor. A battery drives all the circuits. The input circuit can transform the signal into light, and the output circuit again converts the light to the signal.
Advantages
The advantages of optical isolation include the following.
- Original amplitude and frequency is obtained
- Highly linearity
- Modulator or demodulator is not used in the circuit
- Can improve patient safety
Applications
The applications of optical isolation include the following.
- Data acquisition and patient monitoring
- Biomedical measurements
- Ground loop elimination
- Test equipment
Capacitively Coupled Isolation
In this type of amplifier, the digital encoding of input voltage is done. It also allows frequency modulation. The input voltage is transformed into a proportional charge in the capacitor. The device has both modulators as well as a demodulator circuit. The signal of the circuit passes across differential capacitive barriers. We use separate supplies for both sides.
Advantages
The advantages of capacitively coupled isolation include the following.
- Removes ripple noises
- Used in different analog systems
- High linearity
- High stability
Applications
The applications of capacitively coupled isolation include the following.
- Data acquisition
- Patient monitoring
- ECG
- EEG
Features
The main features of an isolation amplifier are as follows:
- Voltage Supply: It is generally referred to as the range of voltage sources.
- Current Supply: It is the amount of current which is drawn from the power supply
- Operating Temperature: It refers to the particular value of ambient temperature at which the amplifier works.
The amplifiers are normally evaluated on the basis of their cost, performance, and size. Along with that, various technical necessities are also taken into account which is linearity, stability, and high-frequency response of the signal. The main problems which arise while designing an isolation amplifier are managing leakage and breakdown voltage.
How to Achieve Isolation?
An operational amplifier or an op-amp has a very high input impedance. This input impedance can be used to cause isolation. When a circuit has a high input impedance, then a very little current is taken from the circuit. From Ohm’s law, we say V=IR. So, greater is the resistance, lower will be the current drawn from the power supply. Thus, because of the high impedance, the op-amp does not draw any significant current from the power supply. As a result, the current taken is very slow. Very little current is transferred from the first half of the circuit to the second. In this way, an op-amp can act as an isolating device between the two parts of the circuit.
Isolation Amplifier Applications
An isolation amplifier can be used for different purposes.
- The uses are mostly determined based on the amplifier design. We can use the isolation amplifier in signal conditioning.
- This utilizes CMO, bipolar, and complementary bipolar amplifiers. The isolation amplifier is selected based on its supply voltage characteristics.
FAQ’s
1). What is an isolated output?
The output produced from the isolation amplifier which is generally isolated from the rest of the circuit is called the isolated output. This isolated output is mostly relay type.
2). Why is isolation required?
Isolation is basically required to prevent power loss. An isolation circuit makes sure that there is no energy loss from the circuit. It uses a high impedance op-amp to make sure that excess current is not drawn from the circuit.
3). What is the isolation barrier?
Isolation barrier refers to that segment of the circuit which prevents the current flow from one part of the circuit to another. It is basically that part of the device which brings about isolation between two parts of a circuit.
4). What is high voltage isolation?
High voltage isolation refers to the voltage which can be applied to a device so that the isolation of the device is not compromised.
5). What is DC isolation?
DC isolation occurs when a part of the circuit is isolated by preventing direct current to flow through it.
Please refer to this link to know more about Amplitude Modulation mCQs.
Thus, this is all about an overview of the isolation amplifier. These amplifiers can isolate a part of the circuit and protect it from electrical damage. It is an extremely important device from an industrial point of view. Can you mention some other important applications of an isolation amplifier?