In our daily life, communication is the most important concept to be discussed. Many of the sources such as TV, internet, mobile, radio, and many others are communication channels. The communication might be either in one-way or two-way and to establish communication there has to be some process. Like the transmitter transmits the signals through the communication medium and the receiver receives the signals. Here, the communication medium is more crucial to make the signals stronger and transmit in the way that we desire. So, the strengthening of the signals can be done through modulation techniques. There are various modulation techniques and the one that has to be discussed is “Phase Modulation”. So, the article describes the process of transmission of signals in PM.
What is Phase Modulation?
Derivation: PM is a type of angle modulation and it is defined as the change in phase of the carrier signal in correspondence with the amplitude of the message signal. Here, both the frequency and amplitude of the carrier signal stays as constant whereas phase varies in accordance. The below figures clearly depict the definition of PM.
The resultant modulated wave has various points where the phase shift takes place. When there is a positive amplitude, the phase varies in one direction, while there is a negative amplitude, the phase varies in other directions. The basic waveform of a phase-modulated wave is as below
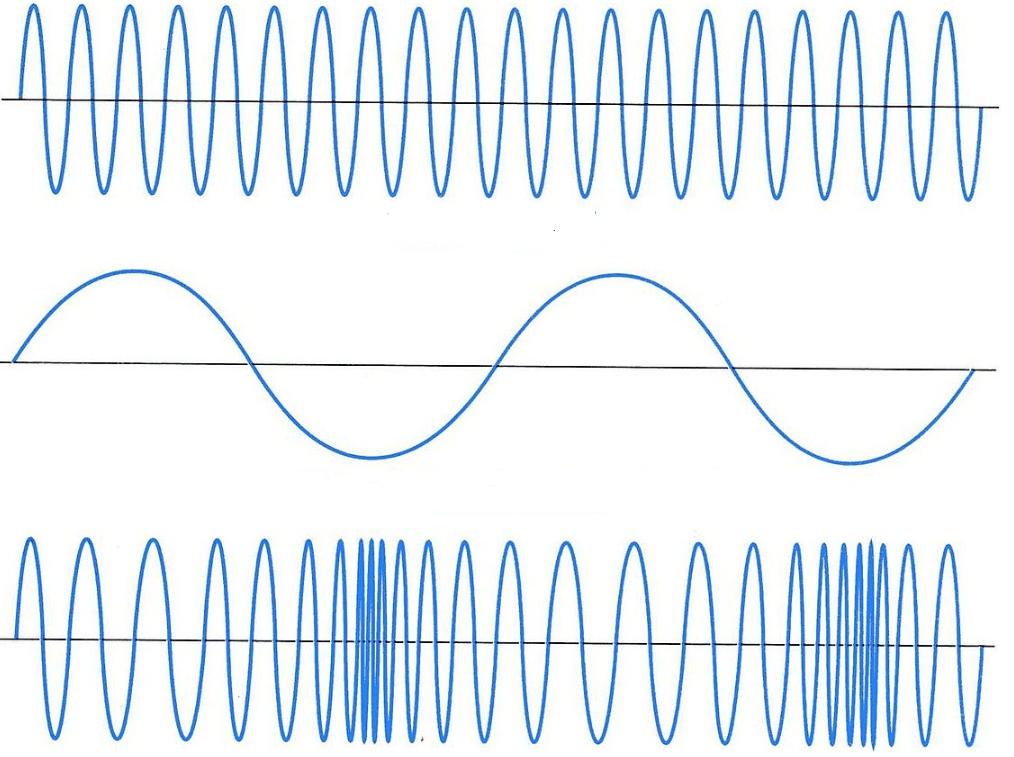
phase-modulation-waveform
Phase Modulated Wave Equation
P(t) = Accos[Wct + kpm(t)]
Here ‘Ac’ represents the amplitude of the carrier signal
‘Wc’ represents the carrier signal’s angular frequency = 2∏fc
And ‘m(t)’ represents the modulating signal
Basic Concepts in Phase Modulation
Let’s be clear on the concept of what is a phase. A radio signal including an oscillating carrier represents the basic sine wave. The continuous amplitude of the sine wave which moves in negative and positive phases and returns to the original point after finishing one full cycle and it is the complete sine wave.
The sine wave movement can also be represented as points in a circle. So, when the phase increases, then the time also progresses and there occurs a phase difference between the points. It operates by modulating the signal’s phase which means that varying the rate where the point revolves around the circle. It is also defined as the speed of rotation across the circle is modulated in correspondence to the mean value.
When the approach of PM is implemented on the signal, the frequency is changed. So, phase and frequency are inseparably associated where the phase is related as the integral of the frequency.
Modulation Index
In the other kinds of modulation techniques, the modulation index is termed as the change in the modulated variable in correspondence with its unmodulated variable. Here, it corresponds to the deviations in phases of the carrier signal. It is denoted as
M.I = ∆ϴ, where ∆ϴ represents the peak phase difference.
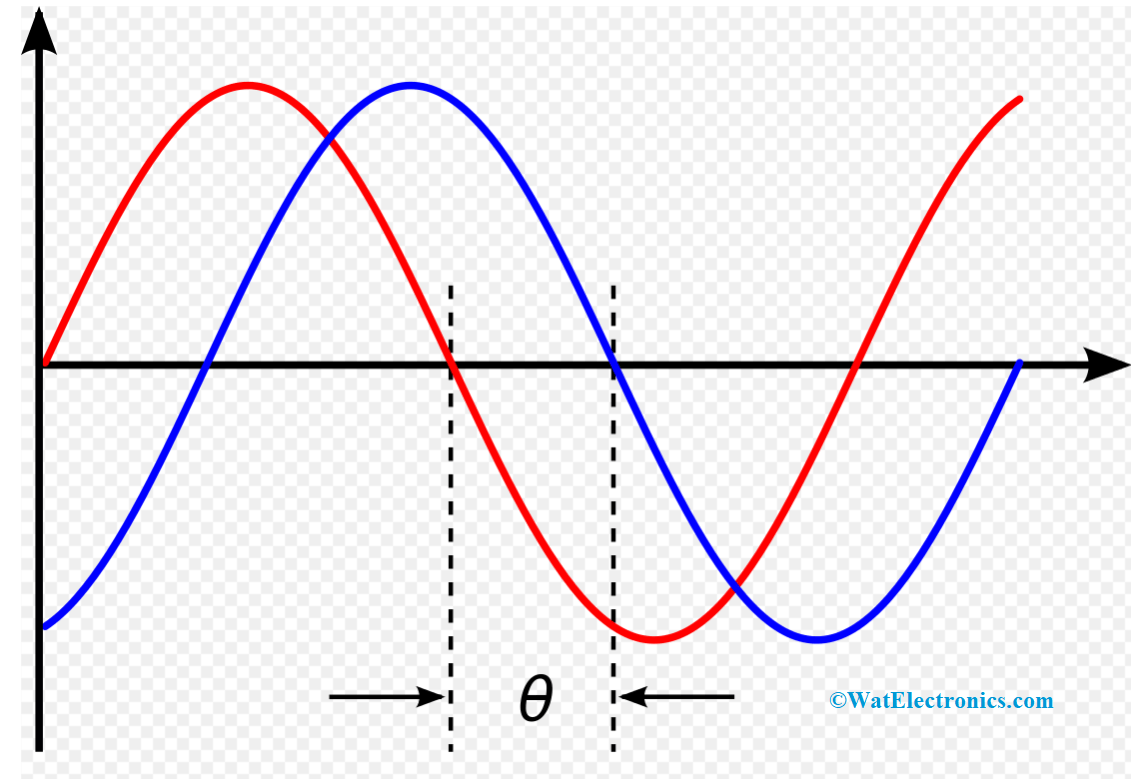
phase-difference-in-PM
Through PM, one can even generate narrowband phase modulation (NBPM) and the equation of it is represented as
ҨP(t) = A cos (wct + kpm(t)).
The above equation can be generated by passing through the below stages
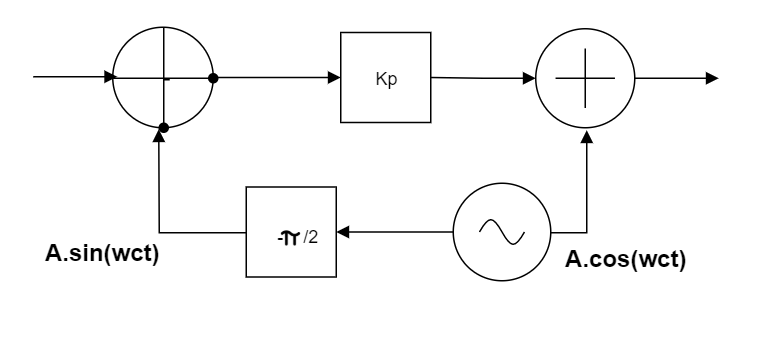
narrow band phase modulation
How PM is Different from Frequency Modulation?
Both PM and FM varies in the below characteristics:
- In PM, phase variation is linearly related to the modulating signal, while in FM frequency variation is linearly related to the modulating signal.
- Noise immunity lies in between AM and FM for phase modulation, and in FM noise exemption is more than that of PM.
- The signal-to-noise ratio is not much better than that of frequency modulation in PM, and in FM signal-to-noise ratio is more.
- Mobile radio services mostly implement phase modulation, and FM is utilized for commercial radio broadcastings.
How PM is Different from Amplitude Modulation?
Both PM and AM varies in the below characteristics:
- PM receivers have greater noise immunity than that of AM, AM receivers are very susceptible to noise.
- In PM, there is the option to enhance noise immunity by enhancing the frequency deviation, whereas in AM no such option exists.
- More requirement for bandwidth and it is based on modulation index, while in AM, bandwidth is lesser to that of FM and PM.
- Both the transmitters and receivers of PM are complicated, whereas AM transmitters and receivers are so streamlined to construct.
- PM modulators are so effective and utilize the whole power and in AM power is wasted as because of sidebands transmission in DSB-SC technique.
Please refer to this link to know more Phase Modulation MCQs
Forms of Phase Modulation
Even though this type of modulation is implemented for analog transmissions, it is extensively applied for digital kinds of modulation as it shifts between various phase angles. This is termed as PSK (Phase Shift Keying) and there exist many kinds in this. Even there exists a kind where the PSK and amplitude keying are combined and that is termed as quadrature amplitude kind of modulation (QAM). Few of the phase shift keying methods are as below:
- Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK)
- Quadrature kind of Phase Shift Keying (QPSK)
- 8 Point of Phase Shift Keying
- 16 Point of Phase Shift Keying
- Offset kind of Phase Shift Keying
These are a few of the types in phase modulation which are mostly applied in radio communications. With the enhancement of current-day radio communication technologies, these all methodologies adopt to shift between various phases thus satisfying all the requirements and conditions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PM
The advantages are
- The foremost benefit of phase modulation is simple to construct the block diagram and easy to implement too.
- Through the Doppler effect, the velocity of the concerned target can be easily found, and this requires a constant carrier that is possible while at the time of phase modulation. This operation does not work in the case of frequency modulation.
- The other unique advantage of phase modulation is signal modulation where it allows for high-speed communication using a telephone system.
- When the data is under transmission having no intrusion, then the rate of speed can be observed.
- This kind of modulation is almost resilient to noise.
The disadvantages are
- This modulation requires two signals to consider the phase difference between the signals. By this, both approaches are necessary where those acts as a signal or as reference.
- Compared to AM and FM modulation techniques, FM requires more hardware equipment to construct because of its conversion approaches.
- There might happen phase uncertainty when the range of index pi radian of modulation is more than 1800
- Through additional equipment called as a frequency multiplier, the phase modulation index can be increased.
Applications of PM
Below are the detailed applications of phase modulation:
- This modulation is mostly implemented in the broadcast of radio waves, and it is the crucial element in many of the digital communication coding methods.
- Phase modulation is extensively utilized for the transmission of radio waves which stands as support for an abundant range of wireless technologies like that of GSM, Satellite television, and Wi-Fi.
- Phase modulation is even employed in digital synthesizers for the generation of both waveforms and signals. This kind of generation is employed in digital synthesizers such as DX7 in Yamaha for phase modulation manufacture application, and Casio CZ for sound synthesis that is termed as phase distortion.
FAQs
1). What do you mean by modulation?
Modulation is defined as the process where the features (either amplitude, phase or frequency) varies in correspondence with the modulating signal.
2). Where do we use phase modulation?
PM is used to encode a data signal as changes in the immediate phase of a carrier wave. It comes under the type of angle modulation.
3). What are FM and PM?
FM and PM modulations are almost similar. In PM, phase changes in proportion with that of modulating signal and in FM phase changes in proportion with the integral of modulating signal.
4). What is PM in networking?
Frequency modulation can be modified to phase modulation by the integration of a CR network with that of a message signal that combines the modulating signal.
5). What is modulation and its need?
The message signals have no capability to travel to long distances and this requires amplification in their features either in amplitude, frequency or phase. The amplification of these variables is called modulation and this process enhances the signal strength and also to enhances the bandwidth and to decreases the size of the antenna.
Please refer to this link to know more about difference b/w GSM and CDMA.
Please refer to this link to know more about Modulation Question and Answers.
With the introduction of digital or data communications, the utilization of phase modulation in the scenario of phase-shift keying has increased very considerably. Formerly there exist few of the benefits for its utilization. And it extensively implemented along with the quadrature amplitude modulation that integrates phase components to its operation along with the amplitude. With data transmissions only set to improve multiple kinds of phase modulation, or methods of modulation which utilize phase elements will go on to enhance. Here the question arises – How amplitude modulation is different in the concepts of phase modulation?