Drift current is the concept involved in a doped semiconductor, there are free charges available, once the voltage is applied we can notice the movement of the charge carriers based on the polarity of the charges it gets attracted towards the respective terminals. Hence the electric field is applied due to which the motion of charge carriers observed results in the production of current. The velocity required for the movement of charge carriers is referred to as drift velocity. In order to … [Read more...]
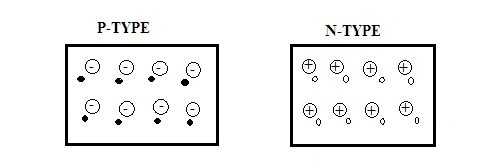
What is an P-type Semiconductor?
A crystal that has its conduction value in between conductor and insulator is termed as the semiconductor.It can be formed by the addition of impurities. It can be referred to as either p-type or n-type. Hence its conduction is based on the types and the amount of impurity added. These solids conduction value is proportional to the temperature value. As the temperature increases its conduction value increases as temperature degrades then the conduction of the semiconductor tends to … [Read more...]
Introduction to PN Junction Theory
When a p-type and n-type interfaced together that leads to the formation of a PN Junction. The commonly suggested semiconductor for this p-n junction is either silicon or germanium based on its preferred electrical properties and its abundance. Basically the p-type and n-type of a semiconductor is formed due to doping impurities. There is an interesting concept evolved from it clearly states that both the p and n regions are conducting until the formation of a barrier. Once it has been formed … [Read more...]
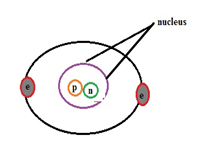
Introduction to the Basics of Atom its Structure and Properties
John Dalton in 1800 was the one who explained regarding the law on multiple proportions. Atom represents the fundamental units that can be divided into subatomic particles. This leads to the development of atomic models. In 1898 Thomson proposed a model by stating that mass of the atom is equally distributed or spread over it but Rutherford's scattering experiment demolishes the statement in 1909. Hence the existence of the nucleus with some electric charge at the center has been estimated … [Read more...]
What is an N-type Semiconductor?
Semiconductors are materials which exhibit properties of both conductors and insulators. The semiconductors are of two types, Intrinsic and Extrinsic Semiconductors. The intrinsic semiconductors are the one with no doping and therefore called as pure semiconductors. The extrinsic conductors are doped with impurity atoms. Based on the type of impurity added they are classified as: N-type and P-type Semiconductors. What is an N-type Semiconductor? A N-type semiconductor is defined as a type of … [Read more...]
Difference Between Intrinsic Semiconductor & Extrinsic Semiconductor
A conductor has a number of charge carriers, which are ready to take part in conduction after a certain voltage or heat is applied. Non-conductors do not have any free charges to take part in conduction even after applying an external voltage or heat. The materials which exhibit properties of both conductors and non-conductors are called semiconductors. The Semiconductor materials behave as an insulator for a certain voltage level and conduct only after the specific voltage level is applied at … [Read more...]
What is Intrinsic Semiconductor and Extrinsic Semiconductor – Energy Band & Doping?
Semiconductor, as the name suggests is a kind of material whose shows properties of both conductors and insulators. A semiconductor material requires a certain level of voltage or heat to release its carriers for conduction. These semiconductors are classified as ‘intrinsic’ and ‘extrinsic’ based on the number of carriers. The intrinsic carrier is the purest form of semiconductor and an equal number of electrons (negative charge carriers) and holes (positive charge carriers). The semiconductor ma … [Read more...]