A BJT or FET both shares the same category of transistors. These transistors have the property of both conduction as well as insulation. BJT, as well as FET, consists of three basic terminals in it. These transistors are found everywhere as the basic components of electronic systems. In this article, we will discuss the basics and comparison between BJT and FET.
It comes under various sizes and with multiple shapes. The main criteria of these transistors is to control the flow of current that passes through one channel by making the variations in the intensity of the currents that are very smaller which flows through the second channel. BJT or FET both have the features resembles to switch as well as amplifiers.
Basics of BJT
BJT stands for bipolar junction transistor. It consists of one p-type and both n-types referred to as n-p-n or one n-type and both p-types referred to as p-n-p. Generally the ideology behind this is two diodes with the p-n junction can be connected in such a way that a bipolar junction has been formed.
The three terminals in BJT can be classified as
- Base
- Emitter
- Collector
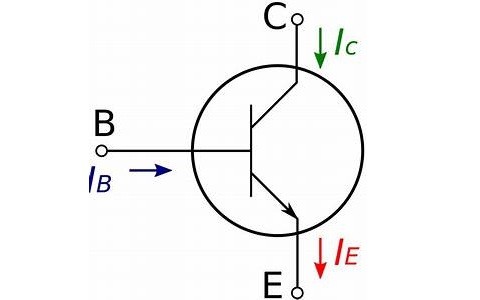
The conduction or the flow of the current can be seen from collector as well as emitter and it is controlled by base terminal.
Basics of FET
It also belongs to the category of transistor that in which the current flow is controlled by the electric field. The operation here is based on one single carrier. However there are two types of charge carriers exist they are electrons and holes. But in the FETs the operation conduction is based on either holes or electrons. Hence these transistors are also referred to as UNIPOLAR transistors.
This transistor also consists of three terminals. They are
- Source
- Drain
- Gate
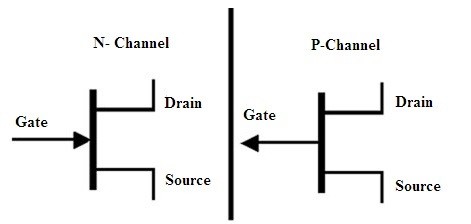
From the terminal source the charges gets involved into the channel. Drain is considered as the terminal for leaving the charges from the channel. Gate is responsible for the channels conductivity modulation.
Please refer to this link to know more about BJT MCQs
Comparison between BJT and FET
The basic comparison between BJT and FET are made as follows
|
BJT |
FET |
|
(1) It is referred to be as a transistor with bipolar junction. |
(1) It is a transistor with uni junction. |
|
(2) In this type of transistor the operation is dependent on both the charge carriers. |
(2) In FET the operation performed is due to the majority of the carriers it may be either electrons or due to holes. |
|
(3) This device is known for its current control. |
(3) This device is known for its voltage control.
|
|
(4) The offset voltage is required. |
(4) There is no requirement of offset voltage. |
|
(5) Consumption of power is more. |
(5) Consumption of power is less. |
|
(6) The gain is more in this type of transistor. |
(6) These transistors gain will be less.
|
|
(7) The output value of impedance becomes
high because of its gain value is high. |
(7) Lesser the gain lesser the value of the
output impedance. |
|
(8) The requirement of low currents makes this transistor in use. |
(8) Low voltage requirements utilize FET. |
Please refer to this for How to Select a Transistor.
Please refer to this link for Field-Effect Transistors MCQs
Please refer to this link to know more about BJT Amplifier
In this way, the comparison is done in between BJT and FET. As per the detailed overview of the differences can you give a practical example for both the transistors BJT and FET?