In a computer network, the network topology is the geometric representation of how different devices, nodes are interconnected logically or physically to each other. There are different ways to arrange a computer network where each has pros and cons based on the requirement of your computer. Some network arrangements can provide you high security and connectivity. In a computer network, there are five types of network topologies like mesh, point to point, star, ring, bus, tree, and hybrid. From that, this article discusses an overview of one of the topologies like bus topology.
What is Bus Topology?
A bus topology is used in a LAN (Local Area Network) where different nodes are linked to a particular cable otherwise a single backbone. A coaxial cable/RJ-45 cable is used to connect different devices. In a bus topology, when the cable has any problem then the entire network will not work. For the safety purpose of a network, there may be alternate cables. This is a very simple type of network topology as compared to other topologies because it can be arranged easily.
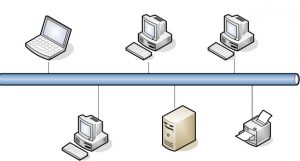
Bus Topology
Bus Topology In Computer Network
In a computer network, bus topology does not require additional cables throughout the installation as compared to other kinds of topologies. If any node within the network stops working then the remaining nodes will keep working. So, it is very convenient to include the latest nodes toward the network without delaying other types of nodes.
For long-distance networking, this kind of topology is not suitable due to data loss. If the nodes are spread in different directions then this kind of topology will not work, so it is better to use other topologies like mesh, star, or ring.
So this topology is applicable for small distance networking. It needs fewer cables as compared to a star topology. If extra devices are added to this topology then the data transfer rate will be slow down. On both faces of the cable, terminators are required. In this network topology, if any error takes place, it is very difficult to detect and solve the issue.
Concepts & Features of Bus Topology
The main concepts covered in the bus topology mainly include backbone cable, terminator, drop link, and node.
Backbone Cable
A backbone cable is nothing but a single cable that is used to connect all the network nodes to this cable so that bus topology will exist. The cable which is used as backbone cable is a coaxial cable. This is the main choice for a network engineer in bus topology. However, we may use a typical Ethernet cable as UTP (Un-shielded Twisted Pair) & STP (Shielded Twisted Pair). If we use fiber optic cable in a bus topology, there are many benefits.
There are many connectors are used based on the cable. If we use Coaxial Cable then Coaxial Cable Connectors are used. If we use STP or UTP, then the RJ45 connector is used and it is the most frequently used connector in these cables. Similarly, fiber connectors are used for fiber optic cable.
Terminator
In a bus topology, a Terminator is one kind of device, used to connect one end of a cable or bus to absorb signals. By using these devices, signal reflection can be avoided, which can generate interference to cause loss of signal. Most of the communication systems like computer buses and networks need some type of termination at the data lane ends, even though this is frequently provided inside through the devices at the data lane ends.
Drop Link
In Bus Topology, a drop Link is a patch cable, used to create a lane for signals to move. Drop link plays a key role in attaching the network node to the backbone cable where one end of the drop link is connected to the backbone and another end is connected to a connector. This connector is connected to the NIC (Network Interface Card) of any network device.
In a computer network, if you want to include a new node, you just need to puncture the cable & connect a drop link to this backbone cable. Likewise, if you want to eliminate an accessible node, then you just need to remove the drop link.
Node
A node is a computer network is a server or client or any other network device. A node plays multiple roles where the decision of role mainly depends on the responsibility and activity. The common roles of this node are client, server, and intermediate node.
In most situations, the Client/Server is a computing device. But, an intermediate node is either a non-computing or computing device. The best example of non-computing devices is Hub, Printer, Switch, and Network Repeater.
Please refer to this link to know more about Bus Topology MCQs
Bus Topology Working
A bus topology is one kind of network topology. This kind of topology includes a single cable at each end with the terminator. This single cable is very useful in connecting all the available nodes. In the network, there is no limit to connect the nodes to the network but these nodes will affect the network performance.
One of the nodes in this topology works like the server so that data can be transmitted from one end to the other in a particular way. Once the data arrives at the endpoint, the terminator will eliminate the data from the line.
In this topology, one major cable works as the backbone for the whole network because this topology holds the transmitted data through the cable. When this data arrives at every node, then the node will verify the address of the destination to notice if it is equal to their address or not.
If the destination address doesn’t equal, then the node will not work more. However, if the destination address of the node equals the address enclosed within the data afterward they process the data. In this topology, the backbone cable mainly depends on the network card which is used at every computer. The connection of this card can be done through a coaxial cable or network cable.
Carrier Sense Multiple Access
For bus topologies, the most frequently used common access technique is Carrier Sense Multiple Access which is also called CSMA. The main function of CSMA is to control the flow of data so that maintenance of data integrity is easy that is, there is no loss of packets. Once two nodes transmit the messages concurrently, and then there are two different methods for handling the issues that occur like CSMA CD & CSMA CA.
CSMA CD: CSMA CD stands for Carrier Sense Multiple Access Collision detection. It is one kind of access method mainly used to notice the collision. Once the collision is noticed, then the sender will not transmit the data. So, it works on after the recovery of collision.
CSMA CA: CSMA CA stands for Carrier Sense Multiple Access Collision Avoidance. It is one kind of access method which is used to stay away from the collision by verifying whether the transmission media is active or not. If it is not active, then the sender remains until the transmission media turns active. This method will effectively decrease the chance of the collision. So it does not work after the collision recovery.
Bus Topology Examples
The examples of bus topology include the following.
- A bus topology is used to connect two floors using a single line.
- A bus topology is used by an Ethernet network
- In this type of network topology, one computer works like a server whereas the other works as a client.
- The main function of the server is to exchange information between different client computers.
- Bus topology network is used to add the printers, I/O devices in the offices or home.
Advantages
The advantages of bus topology include the following.
- Bus topology is a simple topology, used to connect computers or peripherals within a linear manner.
- Simple to understand
- Expanding this topology is easy by connecting two cables.
- If the network is small then this topology works efficiently
- As compared to other topologies, this is very cost-effective.
- As compared to a star topology, the required cable length is less
- Connecting or disconnecting the devices within the network is very easy without disturbing other devices.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of bus topology include the following.
- For large networks, this kind of topology is not applicable
- This kind of topology is extremely slow as compared to others
- Identifying the problems within the network is difficult
- High pocket loss
- Troubleshooting the issues for each device is difficult
- The entire network will split into two parts or damage if the cable gets damaged.
- At both ends of the cable, terminators are necessary
- The network gets slow once extra devices are connected
Please refer to this link to know more about Network Topology MCQs.
Thus, this is all about an overview of bus topology and its working. The main difference between bus and star topology is, in a bus topology, each device can be connected to a backbone cable or single cable whereas, in a star topology, all the devices are connected to the main hub. Here is a question for you, what are the applications of topologies?