The MJE340 is a versatile NPN-type transistor, used in switching, amplification & power control circuits. This transistor provides a reliable and widely available solution for various electronic circuits. But whenever using this transistor within a circuit, then it is suggested to consider some factors like; transient conditions, voltage spikes, etc otherwise it may cause short-term voltage surges. So, proper protective and voltage regulation measures must be implemented to ensure the transistor functioning in its particular voltage range. This article gives brief information on the MJE340 transistor, pinout, specifications, and its applications.
What is MJE340 Transistor?
MJE340 is an NPN silicon-type bipolar junction transistor, available in the TO-126 package. So, this transistor is mainly designed for use in high-voltage applications. This transistor’s maximum collector-base and collector-emitter voltage is upto 300Volts which makes it perfect to utilize in a wide range of higher voltage applications. The max load of this transistor is 500mA or 0.5Amps which makes it to use in any general-purpose high voltage switching-based applications. Its collector dissipation is 20W which makes it perfect to utilize in numerous audio amplification purposes. In addition, it can also be utilized to switch within battery-operated and low-power-based applications.
While looking for a suitable transistor for your application based on a few factors, it is very important to look into a few points on How to Select a Transistor.
Pin Configuration:
The pin configuration of the MJE340 NPN transistor is shown below. This transistor includes three terminals like emitter, a base, and a collector which are discussed below. Thus, this transistor follows simply a particular pinout configuration that decides how the different terminals are positioned. So understanding this pin configuration is necessary for properly connecting it within a circuit & ensuring correct functionality.
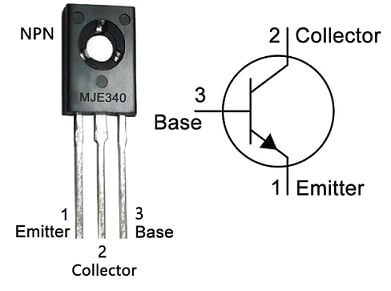
MJE340 Transistor Pin Configuration
Pin-1 (Emitter (E)): The Emitter terminal allows the flow of current into the transistor and is connected to the GND or the common reference point within a circuit.
Pin-2 (Base (B)): The base terminal works as the transistor’s control input. Whenever a small voltage or current is applied to this pin, then its behavior can be easily controlled. This terminal helps in switching the transistor ON/OFF.
Pin-3 (Collector (C)): This is a collector terminal through which the current supplies out of the transistor. This is simply connected to the +Ve voltage supply (or) load in most circuit configurations.
Features & Specifications:
The features and specifications of the MJE340 transistor include the following.
- It is an NPN-type transistor.
- This transistor is available in the TO-126 package.
- Its maximum collector current or IC is 5Amps.
- Collector to emitter voltage or VCE maximum is 300V.
- The collector to base voltage or VCB maximum is 300V.
- The maximum emitter to base voltage or VEBO is 3V.
- Its collector dissipation maximum or Pc is 20 Watts.
- Its transition frequency or fT maximum is 4 MHz.
- DC Current Gain or hFE Min and max ranges from 30 to 240.
- Its storage and operating temperature ranges from -65 to +150 degrees centigrade.
Equivalent & Complementary MJE340 Transistor
Equivalent and replacement transistors of MJE340 transistor are; 2N6175, 2N6177, 2N6176, 2N6557, 2N6559, 2N6558, 2SC1519, 2SC1521, 2SC1520, 2SC1565, 2SC2068, 2SC1749, 2SD668, BD127, 2SD668A, BD128, BD159, BD158, BD232, D40N2, D40N1, D40N3, D40N4KSC2690, , D40N5, KSC2690A, MJE341K, MJE340K, MJE344K, NSD132, NSD131, NSD133, NSD135, NSD134, RCP111A, RCP111D, RCP111C, RCP113A, RCP113C, RCP113B, RCP113D, RCP117B, RCP115B, RCP131C, RCP133C, RCP131D, RCP133D, RCP137B, RCP135B, 40887, 40886 and 40885. The complementary MJE340 PNP transistor is MJE350. Thus, the lead-free version of the MJE340 transistor is the MJE340G transistor.
Replacing a suitable transistor in any circuit based on requirement is very important. To know how to replace it, please refer to this; Replacing Transistors in Electronic Circuits: Factors and Considerations.
How to use MJE340 Transistor Safely in a Circuit for a Long Time?
To get a stable and long-term performance in a circuit with this transistor, we recommend not touching its max specifications limits always. It is always better to stay below 20% at least its max ratings, this rule can be applied to all the transistors. Thus, the maximum load this transistor can handle is 500mAmps so utilize it to drive 400mAmps to be secure The maximum load voltage of this transistor is 300V. So, connect an appropriate heat sink through the transistor & operate and store always in above -65 centigrade & below +150 centigrade temperature.
100Watts Power Amplifier Circuit with Transistors
A power amplifier is a fundamental component within an audio system because it amplifies very weak audio signals to a range to drive speakers to generate clear sound. A 100Watts power amplifier circuit is shown below which uses IRFP244 & IRFP9240 MOSFETs on the output side whereas MJE340 & MJE350 transistors in the driver section & MPSA43 transistor are used in the preamplifier section. The main function of this circuit is to deliver high-quality audio with enough power to effectively drive speakers.
The required components to make this circuit mainly include; Transistors like; IRFP244, IRF9240, MJE350, MJE340, BC546, and MPSA43. Resistors: 39Ω, 390Ω, 1k, 1.5k, 4.7k, 15k, 22k, 33k, 47k, 150k, 330Ω, 10Ω/2W, 0.33Ω/5W and 0.22Ω/10W. Capacitors like; 100nF/100V, 47uF/100V, 470pF/100V, 470nF/63V & 10pF/100V. Miscellaneous like 1N4002, 4Ω 100W Speaker, and ±35 to 40V dual power supply. Connect the circuit as per the diagram shown below.
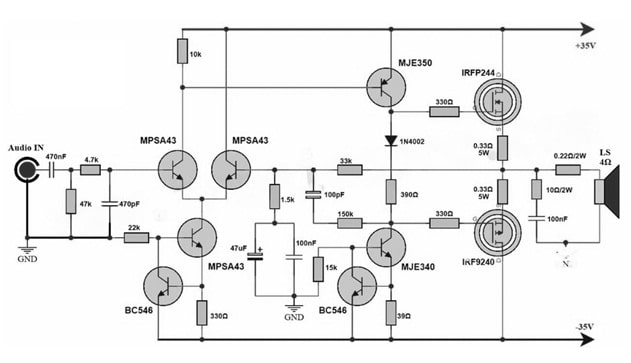
100W Power Amplifier Circuit with Transistors
Working
The 100Watts power amplifier circuit uses a complementary push-pull design with IRFP9240 & IRFP244 MOSFETs within the output stage. This circuit includes two sections like preamplifier section and the driver section. So, the preamplifier section in this circuit includes an MPSA43 transistor which is used to amplify the input audio signals. After that, the driver section includes MJE350 & MJE340 transistors, which provide adequate current to drive the MOSFETs.
This power amplifier circuit works on a ±35Volts dual supply to provide the required power supply to drive the MOSFETs used in the output stage of the circuit. The MPSA43 preamplifier transistor is used to amplify the input signals & feed them toward the driver section which includes both the MJE340 & MJE350 transistors. So transistors provide the necessary current gain to drive effectively the power MOSFETs.
The output stage in the circuit has IRFP9240 & IRFP244 MOSFETs which handle the heavy load current and also deliver the amplified audio signals to the speakers. So these MOSFETs provide low on-resistance by ensuring less power losses & high efficiency. Thus, this circuit amplifies weak audio signals to effectively drive speakers. So each transistor’s specifications in this circuit ensure the proper amplifier circuit functioning by providing the best quality audio output.
Connecting a base resistor to the base terminal of the transistor is mandatory to avoid it being damaged. So, Please refer to this link for; Choosing Base Resistance for Transistors in Electronic Circuits.
MJE340 Transistor Applications
The applications of the MJE340 transistor include the following.
- MJE340 transistor is used to switch & drive higher voltage loads for upto 500mAmps DC.
- This transistor drives various loads within higher voltage circuits like; switch relays, high-power transistors, etc.
- It can also used within low voltage-based batteryworked circuits to drive less voltage LEDs, relays, high ampere transistors, switches, etc.
- It can also used in audio equipment as a separate audio amplifier at its output to drive a speaker directly.
- This transistor is used in UPS circuits, inverter circuits, linear power supplies, motor controllers, switching power supplies, audio amplification, motor controllers, battery chargers, and DC high-voltage switching.
- This transistor is used in audio & other low-power applications as a small-signal amplifier.
- This transistor can be utilized in audio amplifiers, pre-amplifiers, signal conditioning circuits, and other circuits wherever weak signal amplification is necessary.
- It works as a driver transistor within electronic circuits where a high-current drive capability is required.
- Sometimes, it is used in power control circuits because it handles moderate power levels.
- This transistor is used in power supplies, voltage regulators & other applications wherever accurate control above power is necessary.
Please refer to this link for the MJE340 transistor Datasheet.
Thus, this is an overview of the MJE340 transistor which provides complete technical information regarding this NPN BJT like; pinout diagram, thermal characteristics, electrical ratings, etc. It is an important resource, so understanding its limitations and capabilities to use in circuit design & analysis is significant. Integrating the MJE340 transistor in your designs makes it easy to empower your electronic circuits for reliability & exceptional performance. Here is a question for you, what is MJE2955?