Both the BJT and the MOSFET come under the category of semiconductors. This type of devices produces large variations in the electrical signals due to the changes in the applied input signals. The transistors are the revolutionary devices; its invention in the 20th century has bought changes in the electronic systems. These also facilitate to act like switches as well as it can also be used in amplifiers. The basic type in the transistor that introduced earlier is BJT later MOSFET is introduced based on its requirements the various types of transistors are chosen and can be used. This article discusses the difference between BJT and MOSFET
Difference Between BJT and MOSFET
The difference between BJT and MOSFET mainly includes what is BJT, what is MOSFET and their differences.
What is BJT?
BJT stands for Bipolar Junction Transistor. It was invented at the earlier stages. During those days vacuum tubes were used. The replacement for these vacuum tubes is found by the invention of BJT. It has three terminals known as base, emitter, and collector. This type of transistor is generally known for its current control characteristics.
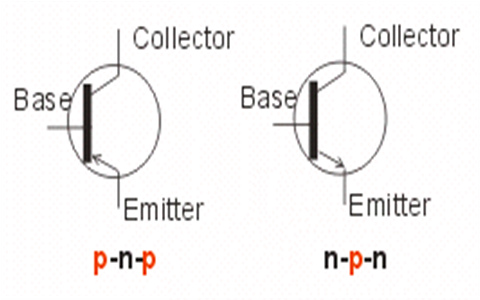
BJT
What is MOSFET?
These devices are also categorized under the semiconductors which are also similar to that of FET. It also consists of three terminals referred to as source, drain, and gate. In this type of device, the current produced at the drain is controlled by the voltage at the terminal referred to as a gate.
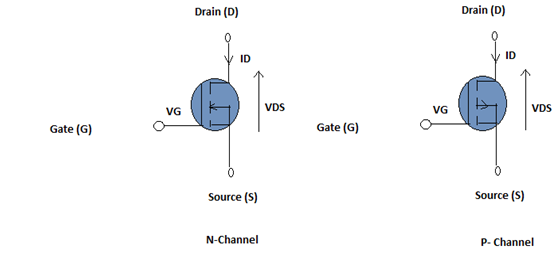
MOSFET
Hence the controlling of current in this device is due to the voltage at the input. This type of device is referred to as a Voltage Controlled Current Device. The working of MOSFET is defined based on depletion and the enhancement modes.
know more about Enhancement MOSFET.
Please refer to this link to know more about BJT MCQs
List of Differences between BJT and MOSFET
The basic difference that defines BJT and MOSFET are as follows
|
BJT |
MOSFET |
|
(1) BJT stands for Bipolar Junction Transistor |
(1) MOSFET is a type of field-effect transistors. It stands for Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor. |
|
(2) BJT is based on its types of P-N junctions connected either it can be NPN or PNP. |
(2) As it is a type of FET in this the transistor can be either made of P-type or N-type semiconductor material. |
|
(3) BJT is known as Bipolar Device. |
(3) MOSFET comes under the category of Unipolar Device. |
| (4) BJT has three terminals collector, emitter and base. |
(4) It also has three terminals known as source, drain, and gate. |
|
(5) These are known as current control devices. |
(5) These are known for its feature of voltage control. |
|
(6) These are preferred during the applications of low current. |
(6) These are preferred during the applications of high current. |
|
(7) The relation between input and output is referred to as be linear. |
(7) The relation between input and output is referred to be non-linear |
|
(8) The size of the device is large compared to that of the MOSFET |
(8) It is smaller in size. |
|
(9) The product between gain and bandwidth is considered to be high. |
(9) The product in between gain and bandwidth is considered below. |
Please refer to this for How to Select a Transistor.
Please refer to this link to know more MOSFET MCQs
Please refer to this link to know more about BJT Amplifier
This is considered to be the basic difference between BJT and MOSFET. Nowadays MOSFET’s are highly preferred over BJT’s for analog as well as digital applications. Can you describe the basic difference between FET and MOSFET?