
8051 Microcontroller Architecture
The 8051 Microcontroller is one of the basic types of microcontrollers, designed by Intel in 1980s. This microcontroller was based on Harvard Architecture and developed primarily for use in embedded systems technology. Normally, this microcontroller was developed using NMOS technology, which requires more power to operate. Therefore, Intel redesigned Microcontroller 8051 using CMOS technology and their updated versions came with a letter C in their name, for instance an 80C51 it is an 8 bit microcontroller. These latest Microcontrollers requires less power to operate as compared to their previous versions. The 8051 Microcontroller has two buses and two memory spaces of 64K X 8 size for program and data units. It has an 8 bit processing unit and 8 bit accumulator units.
8051 Microcontroller Architecture
Following diagram is 8051 Microcontroller architecture . Let us have a look at each part or block of this Architecture of microcontroller.
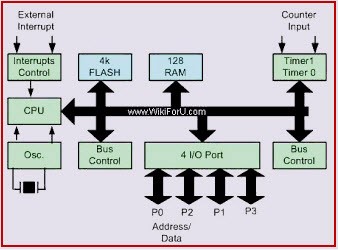
8051 Microcontroller Architecture
Central Processor Unit (CPU)
As we know that the CPU is the brain of any processing device of the microcontroller. It monitors and controls all operations that are performed on the Microcontroller units. The User has no control over the work of the CPU directly . It reads program written in ROM memory and executes them and do the expected task of that application.
Interrupts
As its name suggests, Interrupt is a subroutine call that interrupts of the microcontrollers main operations or work and causes it to execute any other program, which is more important at the time of operation. The feature of Interrupt is very useful as it helps in case of emergency operations. An Interrupts gives us a mechanism to put on hold the ongoing operations, execute a subroutine and then again resumes to another type of operations.
The Microcontroller 8051 can be configured in such a way that it temporarily terminates or pause the main program at the occurrence of interrupts. When a subroutine is completed, Then the execution of main program starts. Generally five interrupt sources are there in 8051 Microcontroller. There are 5 vectored interrupts are shown in below
- INTO
- TFO
- INT1
- TF1
- R1/T1
Out of these, (INT0) ̅ and (INT1) ̅ are external interrupts that could be negative edge triggered or low level triggered. When All these interrupts are activated, set the corresponding flogs except for serial interrupt,.The interrupt flags are cleared when the processor branches to the interrupt service routine (ISR). The external interrupt flags are cleared when the processor branches to the interrupt service routine, provides the interrupt is a negative edge triggered whereas the timers and serial port interrupts two of them are external interrupts, two of them are timer interrupts and one serial port interrupt terminal in general.
Memory
Microcontroller requires a program which is a collection of instructions. This program tells microcontroller to do specific tasks. These programs require a memory on which these can be saved and read by Microcontroller to perform specific operations of a particular task. The memory which is used to store the program of the microcontroller is known as code memory or Program memory of applications. It is known as ROM memory of microcontroller also requires a memory to store data or operands temporarily of the micro controller. The data memory of the 8051 is used to store data temporarily for operation is known RAM memory. 8051 microcontroller has 4K of code memory or program memory,that has 4KB ROM and also 128 bytes of data memory of RAM.
BUS
Basically Bus is a collection of wires which work as a communication channel or medium for transfer of Data. These buses consists of 8, 16 or more wires of the microcontroller. Thus, these can carry 8 bits,16 bits simultaneously. Hire two types of buses that are shown in below
- Address Bus
- Data Bus
Address Bus: Microcontroller 8051 has a 16 bit address bus for transferring the data. It is used to address memory locations and to transfer the address from CPU to Memory of the microcontroller. It has four addressing modes that are
- Immediate addressing modes.
- Bank address (or) Register addressing mode.
- Direct Addressing mode.
- Register indirect addressing mode.
Data Bus: Microcontroller 8051 has 8 bits of the data bus, which is used to carry data of particular applications.
Oscillator
Generally, we know that the microcontroller is a device, therefore it requires clock pulses for its operation of microcontroller applications. For this purpose, microcontroller 8051 has an on-chip oscillator which works as a clock source for Central Processing Unit of the microcontroller. The output pulses of oscillator are stable. Therefore, it enables synchronized work of all parts of the 8051 Microcontroller.
Input/Output Port
Normally microcontroller is used in embedded systems to control the operation of machines in the microcontroller. Therefore, to connect it to other machines, devices or peripherals we require I/O interfacing ports in the microcontroller interface. For this purpose microcontroller 8051 has 4 input, output ports to connect it to the other peripherals
Timers/Counters
8051 microcontroller has two 16 bit timers and counters. These counters are again divided into a 8 bit register. The timers are used for measurement of intervals to determine the pulse width of pulses.
Here is a gist on the 8051 microcontroller architecture which would be handy for a quick reference on its characteristics.
Please refer to this link to know more about 8051 Microcontroller MCQs.
Applications of 8051 Microcontroller
Some of the applications of 8051 is mainly used in daily life & industrial applications also some of that applications are shown below
- Light sensing and controlling devices
- Temperature sensing and controlling devices
- Fire detections and safety devices
- Automobile applications
- Defense applications
Some industrial applications of micro controller and its applications
- Industrial instrumentation devices
- Process control devices
Some of 8051 microcontroller devices are used in measurement applications
- Voltmeter applications
- Measuring and revolving objects
- Current meter objects
- Hand held metering system
Here are some of the 8051 microcontroller based projects that you can go through which would help you to understand better.
8051 Microcontroller Applications in Embedded Systems
The applications of 8051 microcontroller involves in 8051 based projects. The list of 8051 projects is listed below.
- Arduino Managed High Sensitive LDR based Power Saver for Street Light Control System.
- The Temperature Humidity Monitoring System of Soil Based on Wireless Sensor Networks using Arduino.
- RFID based Electronic Passport System for Easy Governance using Arduino.
- Arduino based RFID Sensed Device Access.
- Arduino based DC Motor Speed Control.
- Arduino Based Line Following Robot.
- Zigbee based Automatic Meter Reading System.
- GSM based Electricity Energy Meter Billing with Onsite Display.
- Android Phone Speech Recognition Sensed Voice Command based Notice Board Display.
- Parking Availability Indication System.
- Voice Controlled Home Appliances.
- Remote Control Home Appliances.
- PC Mouse operated Electrical Load Control Using VB Application.
- Solar Highway Lighting System with Auto Turn Off in Daytime.
- 8051 Microcontroller based Wireless Energy Meter.
- Farmer Friendly Solar Based Electric Fence for Deterring Cattles.
- Vehicle Movement Sensed Streetlight with Daytime auto off Features.
Please refer to this link to know more about ARM Architecture & Microcontrollers MCQs
Do you have any innovative ideas to implement the 8051 microcontroller based electronics projects? Then, feel free to share your ideas for getting your project solutions from us and also other readers, by posting in the comments section below.